Black Pepper
Black Pepper
Piper nigrum L.
Family Piperaceae
Pepper Description
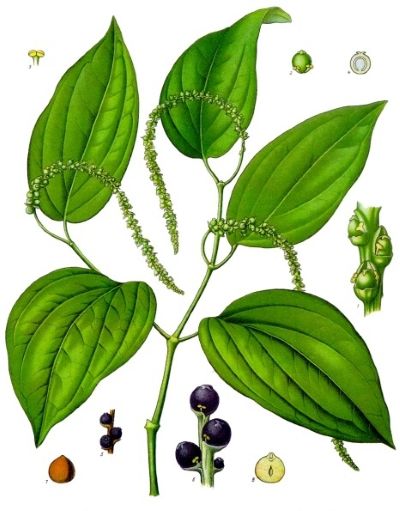
Black pepper is a perennial evergreen vine growing up to 6–10 m long. The root system is branched, superficial, with adventitious roots. Stems are flexible, climbing, clinging to support. Leaves are oval, leathery, 5–10 cm long, dark green, glossy. Flowers are small, white or greenish, gathered in spicate inflorescences 8–14 cm long. Fruits are round drupes, 3–5 mm in diameter, green when unripe, red when ripe, black after drying (black pepper). Ripe fruits without skin produce white pepper. Flowering occurs during the rainy season (June–August), fruiting after 6–8 months. It propagates by cuttings or seeds. Varieties: ‘Malabar’, ‘Tellicherry’, ‘Lampong’, 'Sarawak', 'Muntok'.
Pepper Habitat and Ecology
Black pepper originates from South India (Malabar Coast) and is cultivated in tropical regions (India, Vietnam, Indonesia, Malaysia, Brazil). It prefers loose, well-drained soils (pH 5.5–6.5), partial shade or diffused light, and high humidity. Optimal growing temperature is 25–35 °C, it does not tolerate frost. Yield: 2–5 kg of fruits per plant. Care: watering (15–20 l/m² every 5–7 days), fertilization with organic fertilizers (20–30 kg/m²), protection against fungal diseases (anthracnose) and pepper weevil. It propagates by cuttings (spring) or seeds (rainy season). Environmentally, it enriches the soil, but monocultures can deplete the soil. It can be invasive in tropical regions.
Pepper Raw Materials
Raw materials: fruits (black, white, green pepper), essential oil, less commonly leaves. Fruits are harvested unripe (black pepper) or ripe (white pepper) during the dry season, dried at 40–50 °C (yield 30–35%). Essential oil is extracted by steam distillation from the fruits (yield 2–4%). Leaves are harvested throughout the year, dried in the shade (yield 10–15%). Quality: fruits – black or white, moisture <12%, piperine ≥4%, organic/mineral impurities ≤0.5%, total ash ≤6%; oil – clear, yellowish. Store fruits in airtight containers (2–3 years), oil in dark glass bottles (2 years). The smell of fruits and oil is spicy, pungent; the taste of fruits is pungent.
Pepper Chemical Composition
Fruits: essential oil (2–7%, pinene, limonene, sabinene), piperine (4–10%), alkaloids, resins (1–2%), carbohydrates (30–40%), proteins (10–12%), minerals (potassium, calcium, magnesium). Essential oil: pinene, sabinene, caryophyllene. Leaves: flavonoids, essential oil (0.1–0.5%). Caloric content of fruits: 250–300 kcal/100 g.
Pepper Action and Application
Black pepper has antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, digestive stimulant, and warming effects due to piperine and essential oils. The fruits are used for digestive disorders (flatulence, constipation), colds, to improve blood circulation and metabolism. The essential oil is used in aromatherapy to relieve stress, boost energy, and in inhalations for bronchitis. Leaf infusions have a weak antiseptic effect and are used for skin irritations. In cosmetology, pepper stimulates blood circulation, improves skin condition, and strengthens hair. Externally, the oil is used for massage for muscle pain.
Pepper Application Precautions
Large quantities of fruits (>5 g/day) can cause stomach irritation, burning, or allergic reactions. Essential oil (>2 ml/day internally, undiluted externally) can cause skin or mucous membrane irritation. Store fruits at <12% humidity to prevent mold. For children under 3 years, give infusions at a dose of ≤5 ml/day. Do not combine with blood-thinning medications without consulting a doctor. Avoid applying undiluted oil to sensitive skin. Piperine can enhance the action of certain drugs by increasing their bioavailability.
Pepper Application Contraindications
Pepper is contraindicated in cases of allergy to Piperaceae, peptic ulcer disease, gastritis with high acidity, hemorrhoids, and for children under 1 year of age. External application of the oil is prohibited for eczema, psoriasis, or open wounds.
Pepper Recipes
- Pepper Tea for Colds. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over 1 g of ground pepper, add 10 g of honey, drink once a day for 5 days.
- Leaf Infusion for Dermatitis. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over 10 g of leaves, infuse for 30 min, wipe the skin twice a day for 7 days.
- Inhalation for Bronchitis. Add 3 drops of essential oil to 1 liter of hot water, inhale steam for 10 min, once a day for 5 days.
- Infusion for Flatulence. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over 1 g of ground pepper, infuse for 20 min, drink 50 ml twice a day for 7 days.
- Massage Oil for Aches. Mix 3 ml of pepper essential oil with 20 ml of olive oil, massage muscles once a day for 5 days.
- Pepper and Turmeric Milk for Immunity. Heat 200 ml of milk (dairy or non-dairy) with 1/4 teaspoon ground black pepper and 1/2 teaspoon turmeric powder. Drink warm before bed.
- Black Pepper and Ginger Sore Throat Remedy. In a cup of hot water, add 1/4 teaspoon ground black pepper, 1/2 teaspoon grated ginger, and 1 tablespoon honey. Stir well and sip slowly.
Pepper Cosmetics
Essential oil and ground pepper are used in cosmetology due to their warming and circulatory properties, improving skin and hair condition.
- Hair Mask. Mix 3 ml of pepper essential oil with 20 ml of coconut oil, apply to hair roots, rinse after 20 min, once a week.
- Body Scrub. Mix 2 g of ground pepper with 10 ml of olive oil, massage into skin for 5 min, rinse. Use once a week.
- Skin Tonic. Infuse 1 g of ground pepper in 200 ml of boiling water for 20 min, wipe the skin once a day for 7 days.
- Face Mask. Mix 1 g of ground pepper with 10 g of honey, apply to face for 5 min, rinse. Use once a week.
- Cellulite-Reducing Body Wrap. Mix 5g ground black pepper with 2 tablespoons of coffee grounds and a small amount of carrier oil (like almond oil) to form a paste. Apply to affected areas, wrap with cling film, and leave for 20-30 minutes before rinsing.
- Scalp Stimulating Oil. Combine 2 drops of black pepper essential oil with 1 tablespoon of jojoba oil. Massage into scalp for 5-10 minutes before shampooing to promote circulation and hair growth.
Pepper Culinary Uses
Black pepper is used as a spice in soups, meat and vegetable dishes, sauces, and marinades. Store fruits at 0–5 °C in an airtight container for up to 3 years. Varieties: ‘Malabar’ (for meat dishes), ‘Tellicherry’ (for sauces).
- Pepper Sauce. Mix 2 g of ground pepper with 100 ml of cream, 5 g of garlic, heat to 70 °C, serve with meat.
- Meat Marinade. Mix 3 g of ground pepper with 20 ml of olive oil, 10 ml of soy sauce, marinate meat for 2 hours.
- Pepper Soup. Add 1 g of ground pepper to 500 ml of vegetable soup, boil for 5 min, serve hot.
- Pepper Tea. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over 1 g of ground pepper, add 5 g of ginger, infuse for 10 min, serve warm.
- Spicy Black Pepper Chicken. Sauté chicken pieces with plenty of freshly cracked black pepper, soy sauce, garlic, and a touch of honey until cooked through and caramelized.
- Black Pepper Tofu Stir-fry. Stir-fry cubes of firm tofu with mixed vegetables (bell peppers, broccoli, carrots) and a sauce made from black pepper, soy sauce, rice vinegar, and a hint of sesame oil.
- Black Pepper Crusted Steak. Rub a thick cut of steak generously with freshly cracked black pepper and a little salt before searing or grilling to create a flavorful crust.
- Creamy Black Pepper Pasta. Cook pasta according to package directions. In a separate pan, create a sauce with butter, heavy cream, lots of freshly ground black pepper, and grated Parmesan cheese. Toss with pasta and serve immediately.
Other properties of pepper
Black pepper is used in pharmaceuticals (digestive preparations), perfumery (aromatic oils), and as a natural preservative. The plant is ornamental for tropical gardens. Essential oil is used as an insect repellent.