Cucumber
Cucumber
Cucumis sativus L.
Family Cucurbitaceae Juss.
Description of Cucumber
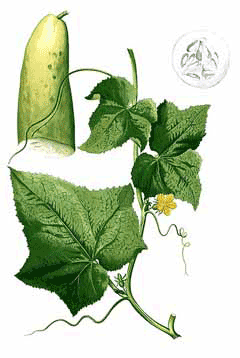
Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) is an annual herbaceous plant, 2–4 m long. The stems are procumbent or climbing, bristly-pubescent, with simple tendrils. Leaves are alternate, long-petioled, triangular-ovate or rounded-pentagonal, 7–20 cm, 3–5-lobed, with unevenly toothed margins. Flowers are unisexual or bisexual, yellowish-orange, up to 4 cm, funnel-shaped, staminate flowers in groups, pistillate flowers solitary, with an elongated inferior ovary covered with spines. Fruits are berry-like, 5–30 cm, cylindrical, barrel-shaped or ribbed, green, with spines or tubercles, turning yellow or brownish upon ripening, flesh juicy, white, slightly greenish. Seeds are oval, flattened, up to 12 mm, white. Internationally known varieties include: 'Burpless', 'Diva', 'Marketmore 76', 'Bush Pickle', 'Lemon', 'Armenian', 'Crystal Apple', 'English Long Greenhouse', 'Gherkin' and '‘Zozulya’ (Зозуля)', '‘German’ (Герман)', '‘Rodnichok’ (Родничок)'. Flowering occurs in May–August (year-round in greenhouses), fruiting in July–September.
Habitat and Ecology of Cucumber
The homeland of the cucumber is India, where wild forms are found climbing trees up to 15–20 m in Northwest India. It has been cultivated for over 6000 years in Asia, Europe, Africa, America, and Australia, both outdoors and indoors, with over 100 varieties. It prefers loose, fertile soils (pH 6.2–6.8), temperatures of 20–30 °C, and watering with 15–20 L/m² every 5–7 days. It does not tolerate frost. It propagates by seeds (sown in April–May). Yield: 20–30 kg/m² (greenhouses), 5–10 kg/m² (open field). Care includes: trellising, fertilizing with nitrogen and potassium (20–30 g/m²), and protection against powdery mildew and aphids. Ecologically, it attracts pollinators and requires crop rotation (after legumes, cabbage).
Cucumber Raw Materials
Raw materials: fruits (fructus Cucumis sativi), leaves (folia Cucumis sativi), seeds (semen Cucumis sativi), flowers (flores Cucumis sativi). Fruits are harvested in July–September (yield 95–98 %) and stored at 5–10 °C. Leaves are harvested in June–August and dried at 30–40 °C (yield 15–20 %). Seeds are collected from overripe fruits in August–September and dried at 25–30 °C (yield 20–25 %). Quality: fruits – green, without rot; leaves – green; seeds – white, moisture <12 %. Store in airtight containers (fruits: 1 month; leaves/seeds: 1 year). The fruits have a fresh aroma, leaves – herbaceous.
Chemical Composition of Cucumber
Fruits: water (90–97 %), carbohydrates (3 %, glucose 1.07–2.7 %), fiber (0.7 %), pectin (0.4 %), organic acids (malic 0.1 %, traces of citric, oxalic), cucurbitacin, ascorbic acid (0.027–7.5 mg %), vitamins (B1: 0.03–0.08 mg %, B2: 0.03–0.04 mg %, B6: 0.03–0.06 mg %, PP: 0.2 mg %, folic acid: 4 mcg %, biotin: 0.27 mcg %, pangamic acid: 0.24–0.27 mg %, β-carotene: 0.06–0.17 mg %, E: 0.1 mg %), proteins (0.8 %), fat (0.1 %), minerals (K: 141 mg %, P: 42 mg %, Mg: 8–14 mg %, Ca: 15–25 mg %, Na: 8 mg %, Cl: 24 mg %, Fe: 0.6 mg %, Al: 0.43 mg %, Cu: 100 mcg %, I: 3 mcg %, Zn: 214 mcg %, Mn: 180 mcg %, Co, Mo: 1 mcg %, F: 17 mcg %). Leaves: ascorbic acid (21.8 mg %). Seeds: fat (0.1 %). Caloric content of fruits: 15–20 kcal/100 g.
Action and Application of Cucumber
Cucumbers stimulate digestion, and have diuretic, laxative, and alkalizing effects due to their high water, fiber, pectin, and potassium content. They are used for constipation, edema, urolithiasis, hypothyroidism, obesity, gout, cardiovascular diseases, and kidney and liver diseases. Juice is used for gastrointestinal colic, coughs, upper respiratory tract catarrh, and burns (externally). Seeds are used for fever, pulmonary tuberculosis, renal colic, and painful urination. Brine is a diuretic, thirst-quenching agent, and helps with hangovers. Externally, fruits and juice treat hemorrhoids, and improve the condition of skin, hair, teeth, and nails. In Tajik medicine, a decoction of roots is used for hepatitis.
Precautions for Cucumber Use
Excessive juice (>500 ml/day) may cause diarrhea or dyspeptic phenomena. Salted/pickled cucumbers increase appetite, cause heartburn, spasmodic pain, and are not recommended for breastfeeding mothers (risk of diarrhea, spasmodic pain in infants). Do not combine fresh cucumbers with soda, lemonade, or milk to avoid dyspepsia. Store raw materials at <12 % humidity. For children under 3 years old, give ≤50 g/day of fresh fruits. Do not combine with retinoids without consulting a doctor.
Contraindications for Cucumber Use
Fresh cucumbers: acute and chronic nephritis (in exacerbation stage), chronic renal failure, urolithiasis (oxalates). Salted/pickled cucumbers: gastritis, stomach and duodenal ulcers, acute and chronic hepatitis, cholecystitis, gallstone disease, hypertension, atherosclerosis, hypothyroidism.
Cucumber Recipes
- Puree for Colitis. Eat 100 g of grated cucumbers on an empty stomach for 7 days.
- Juice for Cough. Drink 50 ml of juice with 10 g of honey 3 times a day for 5 days.
- Seed Infusion for Fever. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over 10 g of seeds, infuse for 30 minutes, drink 50 ml 3 times a day for 5 days.
- Decoction of Vines for Bleeding. Boil 50 g of dried vines in 500 ml of water for 5 minutes, drink 100 ml 3 times a day for 7 days.
- Juice for Edema. Drink 100 ml of juice twice a day for 7 days.
- Pulp for Burns. Apply 50 g of cucumber pulp to the skin for 20 minutes, twice a day for 5 days.
- Cucumber Water for Hydration. Slice 1 cucumber and add to 1 liter of water. Let infuse for at least 30 minutes. Drink throughout the day.
Cucumber Cosmetics
Cucumber juice, pulp, and peel are used for rejuvenation, skin whitening, removing freckles, pigmentation spots, and acne.
- Juice for Rejuvenation. Lubricate the face with juice of overripe cucumbers before bedtime for 30 days.
- Juice for Pigmentation Spots. Lubricate spots with juice of young cucumbers 2–3 times a day for 14 days.
- Lotion for Oily Skin. Grind 200 g of cucumbers, pour 200 ml of vodka, infuse for 7 days, wipe face once a day.
- Infusion for Skin. Grate 300 g of cucumbers, pour 250 ml of vodka, infuse for 14 days, mix with equal amounts of glycerin and water, wipe face once a day.
- Mask for Dry Skin. 50 g of cucumber pulp, 5 ml of lemon juice, apply for 20 minutes, rinse, twice a week.
- Mask for Oily Skin. 50 g of cucumber pulp, 50 g of apple pulp, apply for 20 minutes, rinse, twice a week.
- Under-Eye Treatment. Place chilled cucumber slices over closed eyes for 10-15 minutes to reduce puffiness.
Cucumber Culinary Uses
Cucumbers are used fresh, salted, or pickled for salads, soups, and marinades.
- Salad with Calendula. Mix 200 g of cucumbers, 20 g of calendula flowers, 20 g of green onions, 30 g of sour cream, 1 boiled egg, and salt.
- Salad with Apples. Grate and mix 200 g of cucumbers, 100 g of apples, 30 g of sour cream, 1 boiled egg, and salt.
- Okroshka (Cold Soup). Mix 150 g of cucumbers, 100 g of radishes, 500 ml of kvass, 50 g of herbs, 1 egg, serve cold.
- Marinated Gherkins. Marinate 200 g of gherkins with 100 ml of vinegar and 10 g of salt for 7 days.
- Creamy Cucumber Salad. Slice cucumbers thinly, mix with sour cream or Greek yogurt, fresh dill, and a pinch of salt and pepper.
- Cucumber Raita. Grate cucumber and mix with plain yogurt, roasted cumin powder, and a little salt for a refreshing Indian side dish.
- Cucumber Sandwiches. Thinly slice cucumber and layer on buttered bread with a sprinkle of salt and pepper.
Tips: Use gherkins for marinades, add oil or sour cream for flavor, consume with honey for sweetness.
Other Properties of Cucumber
Cucumbers improve soil in crop rotation. Juice is used in perfumery. Vines are used in phytotherapy.