Cultivated Carrot
Cultivated Carrot
Daucus sativus (Hoffm.) Roehl.
Family Apiaceae — Carrot Family
Carrot Description
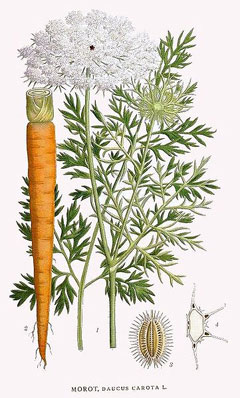
The cultivated carrot is a biennial herbaceous plant, 25–180 cm tall. In the first year, it forms a taproot (conical, fusiform, or cylindrical, 3–5 cm in diameter, up to 30 cm long, yellowish-orange, with transverse slit-like grooves and fibrous roots) and a rosette of pinnately dissected leaves. In the second year, an upright, ribbed, hollow, branched stem develops. Leaves are alternate, bipinnate or tripinnate, up to 20 cm, triangular or ovoid; lower leaves are long-petioled, upper ones are sessile, covered with stiff hairs. Flowers are small, whitish, reddish, or greenish, in compound umbels (10–15 rays), with notched petals and a curved lobe. Fruits are elongated-ovoid schizocarps, 3–4 mm, with spines. Flowering occurs from June to July, and fruiting from August to September. Popular varieties include ‘Nantes’, ‘Chantenay’, and ‘Vitaminna 6’. Taproots are harvested in September–October.
Habitat and Ecology of Carrot
Carrots originated in Persia (10th century). They are cultivated universally in Europe, North America, Asia, and Australia, with numerous varieties. They prefer loose, fertile soils (pH 6.0–7.0), moderate watering (10–15 l/m² once every 7 days), temperatures of 18–25 °C, and can withstand frosts down to -5 °C. They are propagated by seeds (sowing in March–May or October). Yield: 4–8 kg/m². Care: loosening, fertilization with nitrogen and potassium (20–30 g/m²), protection against carrot rust fly and phomopsis. Ecologically, they improve soil during crop rotation (after cabbage, potatoes) and attract pollinators.
Carrot Raw Materials
Raw materials: taproots (radix Dauci sativi), leaves (folia Dauci sativi), seeds (semen Dauci sativi). Taproots are harvested in September–October, stored at 0–2 °C, layered with sand (yield 90–95 %). Leaves are harvested in June–July, dried in the shade at 30–40 °C (yield 10–15 %). Seeds are collected in August–September by cutting the umbels, dried at 25–35 °C (yield 20–25 %). Quality: taproots — orange, no rot; leaves — green; seeds — gray-brown, moisture <12 %. Store in airtight containers (taproots: 6 months, leaves/seeds: 2 years). The smell of taproots is sweetish, seeds are spicy.
Chemical Composition of Carrot
Taproots: sugars (4.5–15 %, glucose), fiber, pectin (0.8 %), ascorbic acid (0.5 mg %), vitamins (B1 up to 0.1 mg %, B2 up to 0.05 mg %, PP up to 1.47 mg %, folic acid up to 0.1 mg %, E, K), carotenoids (up to 25 mg %, beta-carotene, alpha-, gamma-, epsilon-carotene, phytoene, lycopene), flavonoids (up to 60 mg %, rutin), coumarins (umbelliferone), sterols (daucosterol), essential oil (1.6 %, pinene, limonene, geraniol, citral), minerals (K, Ca, Fe, P, Co, Mg, Cu, I, B). Leaves: daucin, pyrrolidine, anthocyanins, quercetin, kaempferol. Seeds: essential oil (1.6 %, pinene, geraniol, citral, asarone), fatty oil (13 %, petroselinic, oleic acids), flavonoids (chrysin, apigenin), coumarins, furocoumarins (xanthotoxin), alkaloids. Caloric content of taproots: 35–40 kcal/100 g.
Action and Application of Carrot
Taproots are rich in beta-carotene, improving vision, hematopoiesis, metabolism, strengthening blood vessels, and having diuretic, wound-healing, anti-inflammatory, anthelmintic, and laxative effects. They are used for avitaminosis, anemia, hypoacid gastritis, kidney stones, osteochondrosis, bronchitis, obesity, allergies, pulmonary tuberculosis, after myocardial infarction, and during pregnancy and lactation. Juice is used for stomatitis, tonsillitis, oral thrush in children, and strengthens vision. Seeds are diuretic, antispasmodic, carminative, used for flatulence, angina pectoris, and kidney stones. Externally, carrot pulp treats burns, ulcers, and purulent wounds. Essential oil and dry extract of fruits ('Daucarin') dilate coronary vessels, used for atherosclerosis and angina pectoris.
Precautions for Carrot Use
Excessive juice (>500 ml/day for adults, >100 ml/day for children) can cause hypervitaminosis A (yellowing skin, nausea, liver dysfunction). Seeds (infusions >200 ml/day) can increase diuresis, leading to dehydration. Store raw materials at humidity <12 %. For children under 3 years, give <=50 ml/day of juice. Do not combine with retinoids without consulting a doctor.
Contraindications for Carrot Use
Exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease, enteritis, allergy to Apiaceae, kidney stones (oxalates), hyperthyroidism, and children under 1 year of age.
Carrot Recipes
- Juice for Vitamin Deficiency. Drink 100 ml of juice with 10 g of honey twice a day for 7 days.
- Pulp for Burns. Apply 50 g of grated carrot to the skin for 20 min, twice a day for 5 days.
- Seed Infusion for Flatulence. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over 10 g of seeds, steep for 8 hours, drink 50 ml three times a day for 5 days.
- Seed Powder for Kidney Stones. Take 1 g of seed powder three times a day for 7 days.
- Juice for Bronchitis. Drink 100 ml of juice with 15 g of honey three times a day for 7 days.
- Juice for Vision. Drink 100 ml of juice with 5 ml of olive oil once a day for 14 days.
- Roasted Carrots with Honey Glaze. Toss chopped carrots with olive oil, honey, salt, and pepper. Roast at 200°C (400°F) until tender and slightly caramelized.
- Carrot and Ginger Soup. Sauté chopped carrots and ginger, then simmer in vegetable broth until soft. Blend until smooth and season to taste.
Carrot Cosmetics
Carrot juice and pulp are used for skin and hair, for whitening freckles, and strengthening hair.
- Face Mask. 30 g of grated carrot, 5 ml of lemon juice, apply for 15 min, rinse off, twice a week.
- Hair Lotion. 20 ml of carrot juice, 10 ml of olive oil, rub into the scalp, once a week.
- Mask for Freckles. 20 g of carrot pulp, 10 g of sour cream, apply for 10 min, rinse off, twice a week.
- Face Scrub. 20 g of grated carrot, 10 g of honey, 5 g of sugar, apply for 5 min, rinse off, once a week.
Carrot Culinary Uses
Carrots are used raw, boiled, dried, pickled, and canned for salads, soups, patties, juices, marinades, and liqueurs. Seeds are used as a spice.
- Salad. 200 g of grated carrot, 50 g of apples, 20 ml of olive oil, dress with lemon juice.
- Cream Soup. 300 g of carrots, 200 g of potatoes, 1 l of broth, boil for 20 min, puree, serve with herbs.
- Patties. 200 g of grated carrot, 50 g of semolina, 1 egg, fry for 10 min, serve with sour cream.
- Juice. Pass 300 g of carrots through a juicer, drink chilled, once a day.
- Carrot Cake. A classic dessert made with grated carrots, spices, and a cream cheese frosting.
- Carrot Fritters. Grate carrots, mix with flour, egg, and spices, then pan-fry until golden brown.
Tips: Mix with oil for better carotene absorption, store root vegetables in a cool place. Sauté with sugar for coloring dishes.
Other Properties of Carrot
Taproots improve soil during crop rotation. Seeds are used in perfumery (essential oil). Leaves are used in herbal medicine.