Common Corn (Maize)
Common Corn (Maize)
Zea mays L.
Family Poaceae (Gramineae)
Description of Corn
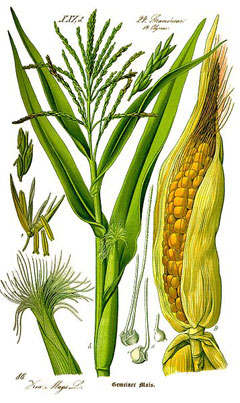
Common corn is an annual herbaceous plant, cultivated, not found in the wild. The root system is fibrous, penetrating to a depth of 1–2 m, with prop roots at the base in high humidity. Stems erect, 1–5 m tall, 3–6 cm thick, with nodes and loose pith, unbranched (rarely branched at the base), sometimes woody below. Leaves linear-lanceolate, 50–100 cm long, 5–12 cm wide, alternate, with wavy, ciliate edges, slightly pubescent above, with a sheath enveloping the stem. Flowers unisexual, inconspicuous, without perianth: staminate (6–14 mm) gathered 1–3 in spikelets, forming terminal panicles (20–50 cm); pistillate in ears (1–3 per stem), enclosed by bracts, with long (up to 20 cm) pubescent styles-stigmas. Fruit compressed-rounded or kidney-shaped caryopsis, 5–12 mm, yellow, white, red or purple, gathered in ears (100–1000 grains). Flowering in July–September, fruiting in September–October (in mid-latitudes fruits may not ripen). Propagated by seeds. Varieties: ‘Golden Fleece’ (sweet), ‘Pioneer’ (dent), ‘Gourmet’ (sweet).
Distribution and Ecology of Corn
Corn originates from Southern Mexico and Guatemala, where it was cultivated 7–10 thousand years ago. Today grown worldwide in warm and temperate zones (America, Africa, Asia, Europe). Prefers loose, fertile soils (pH 6.0–7.0), well-drained. Requires 8–10 hours of sunlight and temperatures 20–30 °C, does not tolerate frosts below -2 °C. Propagated by seeds (sowing in April–May, depth 4–6 cm). Yield: 5–10 t/ha (grain), 20–50 t/ha (silage). Care: watering (15–20 L/m² every 5–7 days), feeding with nitrogen-phosphorus fertilizers (30–40 g/m²), weeding, protection from corn borer and fusarium. Ecologically improves soil in crop rotation (3–4 years), but depletes in monoculture. Can be invasive with self-seeding in tropics.
Raw Materials from Corn
Raw materials: corn stigmas and styles (styli et stigmata Maydis), grains, oil (oleum Maydis), pollen. Stigmas harvested in August–September (milk-wax ripeness), hand-picked or cut, dried at 35–40 °C in 1–2 cm layer (yield 20–25%). Grains harvested in September–October, dried at 30–35 °C (yield 80–85%). Oil extracted from grain germs (yield 5–7%). Pollen harvested in July–August, dried at 30 °C (yield 10–15%). Quality: stigmas golden-brown, moisture <13%, blackened ≤3%, organic/mineral impurities ≤0.5%, total ash ≤7%, extractives ≥15%; grains mold-free, moisture <12%; oil golden-yellow, clear; pollen yellow, impurity-free. Store stigmas and pollen in cloth bags (15–30 kg, 2–3 years), grains in dry containers (1–2 years), oil in dark bottles (1 year). Stigmas aroma weak, taste sweetish, mucilaginous; oil neutral taste.
Chemical Composition of Corn
Stigmas and styles: vitamins (K up to 1.6%, C, B1, B2, B6), nicotinic, pantothenic acids, inositol, carotenoids (incl. cryptoxanthin), saponins (3%), sterols (sitosterol, stigmasterol, beta-sitosterol glycoside), essential (0.12%) and fatty oil (3%), glycokinins, phytohemagglutinins, allantoin, resinous (3%) and gum-like substances (38%), phenolic carboxylic acids, bitter glycosides (1.5%), flavonoids, alkaloids (0.5%), tannins, maltose, glucose. Grains: starch (up to 61.2%), pentosans (7.4%), proteins (8–10%), vitamins (B1, B2, B6, E, biotin, provitamin A), quercetin, minerals (potassium, sodium, calcium, phosphorus, iron, gold). Oil: vitamin E, linoleic acid (50–60%), sterols. Pollen: proteins, vitamins (B, C), phytohormones. Calorie content of grains: 300–350 kcal/100 g.
Effects and Applications of Corn
Corn stigmas and styles have choleretic (increase bile secretion, reduce viscosity and bilirubin), diuretic, hemostatic (increase platelets in hypoprothrombinemia), anti-inflammatory, hypoglycemic, antitumor, and sedative effects. Promote dissolution of stones (carbonates, urates, phosphates) in kidneys and ureters, effective against tapeworms. Used for cholecystitis, cholangitis, hepatitis, cholelithiasis, enterocolitis, edema (cardiac/renal origin), urolithiasis, nephritis, cystitis, prostatitis, prostate adenoma, hypertension, glaucoma, obesity, atherosclerosis, hemorrhagic diatheses, uterine and nasal bleedings, hemorrhages in vitreous body and conjunctiva, liver diseases. Decoction used for edema and weeping dermatitis. Corn oil lowers cholesterol, effective in vitamin E hypovitaminosis. Pollen biostimulant and sedative for anemia, chronic constipation, children's diarrhea, gastritis, enteritis, prostatitis, prostate adenoma. Grains included in diets for diabetes, heart and vascular diseases.
Precautions for Using Corn
Infusions and decoctions of stigmas (>100 ml/day) may cause diarrhea or allergic reactions. Oil in doses >75 g/day may disrupt lipid balance. Pollen contraindicated in pollen allergy (risk of anaphylaxis). Prolonged use (more than 1 month) may increase blood clotting due to vitamin K. Store stigmas at humidity <13% to prevent mold. Give children under 3 years infusions in doses ≤10 ml/day. Do not combine with anticoagulants (warfarin, aspirin) without doctor's consultation.
Contraindications for Using Corn
Corn is contraindicated in reduced appetite, low body weight, thrombophlebitis, increased blood clotting, allergy to cereals, peptic ulcer, acute pancreatitis, children under 1 year. External use of oil prohibited in eczema or psoriasis. Do not combine with warfarin or aspirin.
Recipes with Corn
- Infusion for Cholecystitis. Pour 10–15 g stigmas with 200 ml boiling water, infuse 1 hour, drink 50 ml 3–4 times a day 10–15 min before meals, 2 weeks.
- Decoction for Urolithiasis. Boil 15 g stigmas in 500 ml water 3 min, infuse 2 hours, drink 50 ml 3 times a day before meals, 3 weeks.
- Infusion for Allergic Dermatitis. Infuse 10 g stigmas in 200 ml boiling water 1 hour, take 1 tbsp every 3 hours, 5 days.
- Extract for Cholecystitis and Urolithiasis. Liquid extract (70% ethanol) take 30–40 drops 2–3 times a day before meals, 2 weeks; store in dark place.
- Collection for Cystitis. Boil 10 g stigmas, 10 g bearberry, 10 g bean pods in 1 L water 15 min, drink 150 ml 6 times a day with salt-free diet, 5 days.
- Pollen for Anemia and Prostatitis. Mix 1–3 tsp pollen with 1 tsp honey, take 2–3 times a day, 2 weeks (if no allergy).
- Oil for Atherosclerosis. Take 20–25 g oil 2–3 times a day 30–60 min before meals, 1 month.
- Decoction for Edema. Boil 10 g stigmas in 200 ml water 10 min, drink 1–2 tbsp every 3 hours, 7 days.
Cosmetics from Corn
Corn oil and stigmas used in cosmetology due to vitamin E and antioxidants, moisturize skin and hair, give hair golden hue.
- Face Mask. Mix 10 ml corn oil with 1 tsp honey, apply to face for 15 min, rinse. Use 1 time a week.
- Hair Rinse. Infuse 15 g stigmas in 500 ml boiling water 1 hour, use after washing for golden hue, 2 times a week.
- Body Scrub. Mix 20 g corn flour with 10 ml oil, massage skin 5 min, rinse. Use 1 time a week.
- Hand Oil. Rub 10 ml corn oil into hand skin before bed, 2 weeks.
Culinary Uses of Corn
Corn grains boiled, fried, canned, processed into flour, groats, oil or malt (contains vitamins B, E, phytohormones, enzymes, maltose, amino acids). Varieties: ‘Golden Fleece’ (for boiling), ‘Gourmet’ (canning). Store ears at 0–5 °C no more than 2 weeks. Boil young corn 15–20 min, old 40–60 min; rinse grains for crumbliness.
- Boiled Corn. Boil 2 ears in 1 L water 20 min, serve with salt and butter.
- Corn Porridge. Boil 200 g groats in 600 ml water 30 min, add 20 g butter, salt.
- Salad with Corn. Mix 100 g canned corn with 50 g cucumbers, 50 g tomatoes, 10 ml corn oil, salt.
- Popcorn. Fry 100 g grains in 20 ml oil 5 min, sprinkle with salt or sugar.
Other Properties of Corn
Corn forage and industrial crop (starch, alcohol, oil). Used in crop rotation, but depletes soil in monoculture. Leaves and stems used for silage.